The Remarkable 35% Rule: How Computer Hardware Defies Economic Norms
- Ctrl Man
- Technology , Economics
- 12 Jul, 2024
The Remarkable 35% Rule: How Computer Hardware Defies Economic Norms
I. Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, there is an astonishing trend that has captured the imagination and attention of both industry insiders and casual observers alike—the consistent annual price reduction of computer hardware by approximately 35%. This phenomenon, known as the “35% rule,” defies traditional economic norms and challenges our understanding of technological progress.
A. The Astonishing Trend in Computer Hardware Pricing
When one considers the rapid advancements made in computing technology over the past decades, it’s remarkable how affordable computers have become. From the exorbitant costs of early mainframes to today’s sophisticated laptops and smartphones, the price per unit has drastically reduced while performance and capabilities have significantly increased.
B. Brief Explanation of the 35% Annual Price Reduction
The core reason for this unique trend lies in a combination of factors that have historically driven down hardware prices at an almost unprecedented rate. This steady reduction—approximately 35% annually since the early ’70s—has been a fascinating economic anomaly, particularly when compared with other sectors and even within computing itself.
II. Understanding the 35% Rule
A. Historical Context (1977 to Present)
The trend began in earnest during the late 1970s, coinciding with the rise of microprocessors, which were instrumental in driving down costs and increasing performance. The introduction of personal computers by companies like Apple and IBM further propelled this revolution.
B. Comparison of Price Drops in Different Computer Components
1. Hard Drives
Hard disk drives saw a significant price decrease over the years, with advancements in storage density and efficiency making larger capacities more accessible to consumers at lower prices.
2. RAM
The cost per gigabyte of Random Access Memory (RAM) has plummeted as production techniques improved, allowing for denser memory chips that consume less power while offering more capacity at a cheaper rate.
3. Processors
CPUs have witnessed an even more dramatic price reduction, with Moore’s Law playing a pivotal role in driving this trend. This law predicts the exponential growth of computing capabilities over time, alongside a decline in cost per transistor.
C. The Consistency and Predictability of the Trend
The 35% rule is not just a fluke or an anomaly; it’s been remarkably consistent across different hardware components and spans decades. This trend suggests that there are fundamental economic forces at play that continuously push computer hardware prices down, making it one of the most intriguing phenomena in technology economics.
III. The Driving Forces Behind the 35% Rule
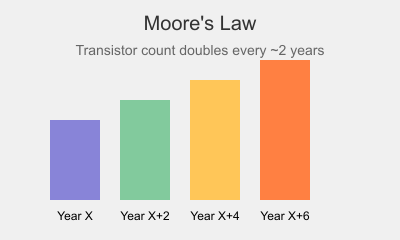
A. Moore’s Law and Its Impact
Perhaps the single most influential factor is Moore’s Law, which posits that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles about every two years while the cost per transistor halves. This has driven not only performance increases but also price reductions in hardware components.
B. Technological Innovations
Advancements in semiconductor technology and materials science have been crucial for achieving higher densities, better efficiencies, and smaller sizes of computer components, all contributing to lower costs.
C. Economies of Scale in Production
As the demand for computing power has grown, so has the ability for manufacturers to produce hardware at larger scales. This scale-up often leads to cost savings that are then passed on to consumers through reduced prices.
D. Market Competition
The fierce competition among tech giants and innovative startups has driven innovation, pushing companies to develop more efficient processes and technologies to maintain their market share and attract consumers with lower-priced products.
IV. Case Study: Hard Drives
A. Price per MB in 1977 vs. 2024
The price per megabyte (MB) of storage capacity has dramatically decreased over time, reflecting a substantial improvement in storage density and efficiency. For example, in 1977, storing 1MB of data cost about $1,000. Today, the same storage costs approximately $0.0000238 per MB.
B. Technological Milestones in Hard Drive Development
Advancements like moving heads, multi-level cell technology, and solid-state drives have revolutionized hard drive storage, offering faster speeds, greater capacities, and lower energy consumption at reduced costs.
C. Impact on Data Storage and Computing Capabilities
As the cost of storage has decreased, there has been a corresponding increase in data processing capabilities. Smaller businesses can afford larger storage solutions without breaking the bank, while researchers have access to massive datasets for their work.
V. Beyond Computer Hardware: Other Industries
A. Photovoltaic Panels and Their Price Trend
Similar to computer hardware, photovoltaic panels have seen a significant price reduction over time, driven by advancements in manufacturing techniques, economies of scale, and increased competition in the renewable energy sector.
B. Comparison with Other Technological Products
While other industries may also exhibit similar trends, the rapid pace at which computer hardware prices fall makes it stand out as an exceptional economic phenomenon.
C. Why Computer Hardware Stands Out
Computer hardware’s price reduction trend is not just a byproduct of technological progress; rather, it reflects the interplay between innovation, manufacturing efficiencies, and market dynamics that are unique to this sector.
VI. The Future of the 35% Rule
A. Current Challenges to Moore’s Law
As we approach the physical limits of miniaturization, challenges like quantum computing and alternative processing techniques may become more prominent as drivers for technological advancements in the future.
B. Potential New Technologies to Maintain the Trend
Quantum computing, neuromorphic engineering, and 3D chip stacking are among the new technologies that might help maintain or even extend hardware price reductions beyond traditional semiconductor advancements.
C. Predictions for the Next Decade
Over the next decade, expect continued refinement in existing technologies alongside the emergence of disruptive innovations. The future of computer hardware pricing remains intriguing as it is shaped by a confluence of factors that are reshaping not just computing but technology at large.
VII. Conclusion
A. The Unprecedented Nature of This Economic Trend
The 35% rule, an anomaly in economic history, underscores the remarkable intersection of technological progress and market forces. It challenges our understanding of how innovation can be economically sustainable on a macro scale.
B. Implications for Future Technological Development
As hardware prices continue to fall, it opens up unprecedented opportunities for education, research, and everyday applications that were once out of reach. The democratization of technology is likely to accelerate further as the cost barrier decreases.
C. The Ongoing Revolution in Computing Power and Affordability
The 35% rule represents more than just a historical footnote; it’s an ongoing revolution in computing power that is making technological advancement not only possible but affordable for everyone. As we move forward, this trend could reshape industries from healthcare to entertainment, driving innovation and expanding the frontiers of what’s feasible with technology.
- This article draws inspiration from Clayton M. Christensen’s groundbreaking work, The Innovator’s Dilemma